PI-RADS v2
Multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) is increasingly used for prostate cancer diagnosis and guiding biopsies. Multiparametric MRI is a combination of T2-weighted, Diffusion and dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging and is an accurate tool in the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer. However, there is a lot of variation in image acquisition.
The introduction of the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) classification for prostate MRI in 2012 lead to a more standardized acquisition, interpretation and reporting of prostate MRI. Since then, this classification system has been revised and simplified in 2015 and is still evolving, based on data analysis of multiparametric prostate MRI. The most recent mpMRI acquisition protocol and interpretation guidelines were recently recommended by American College of Radiology and European Society of Urogenital Radiology in the consensus guidelines: Prostate Imaging - Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS v2) [1]. The PI-RADS assessment category determines the likelihood of clinically significant prostate cancer, which is defined as a tumor with a Gleason score of 7 or more.
| PI-RADS Score | Meaning | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Very low | Clinically significant cancer is highly unlikely to be present |
| 2 | Low | Clinically significant cancer is unlikely to be present |
| 3 | Intermediate | The presence of clinically significant cancer is equivocal |
| 4 | High | Clinically significant cancer is likely to be present |
| 5 | Very high | Clinically significant cancer is highly likely to be present |
Assignment of a PI-RADS assessment category for each lesion is based on the scoring of T2w, DWI/ADC, and DCE sequences, according to zonal anatomy.
PI-RADS v2 Assessment: Peripheral Zone (PZ)
| DWI | DCE | PI-RADS |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | |
| 2 | 2 | |
| 3 | - + |
3 4 |
| 4 | 4 | |
| 5 | 5 |
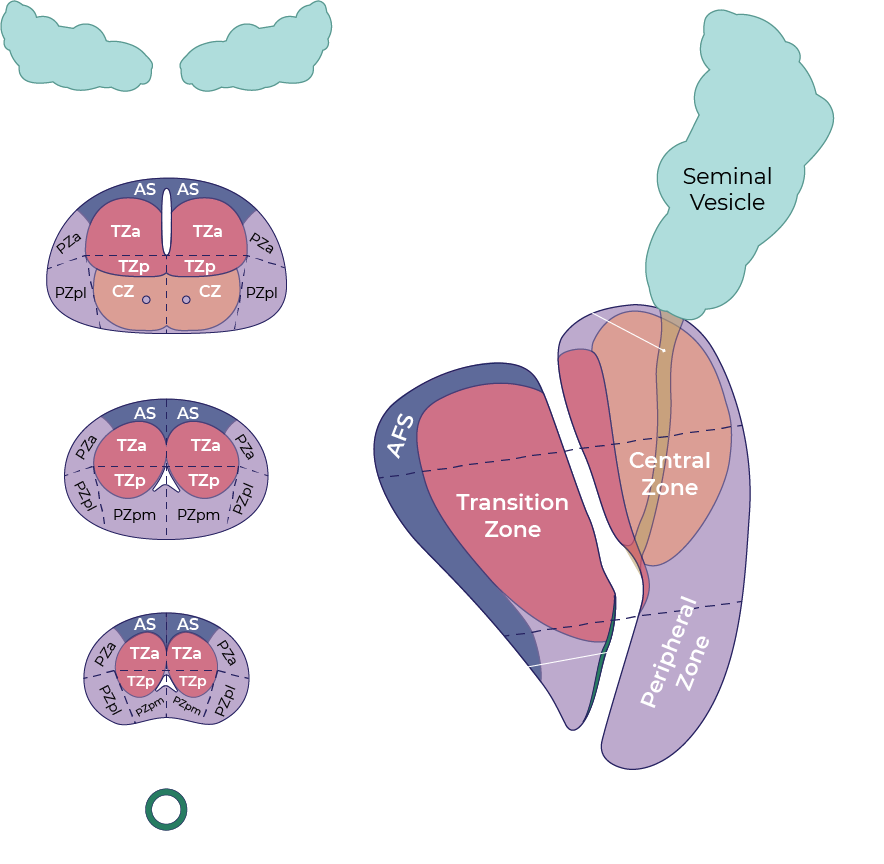
The peripheral zone is situated on the posterior and lateral side of the prostate, surrounding the transition zone. For the peripheral zone the DWI/ADC is the primary determining sequence (dominant sequence) to assign the PI-RADS assessment category. Since the dominant sequence for PI-RADS assessment in the peripheral zone is different from the transition zone, identification of the zonal location of a lesion is vital. In the peripheral zone an equivocal lesion (PI-RADS category 3) is assigned to PI-RADS category 4 if DCE is positive, i.e focal or earlier contrast enhancement. The lesion remains assigned to PI-RADS category 3 if the DCE is negative, i.e. no early enhancement or diffuse enhancement and not corresponding to the focal T2W / DWI lesion or focal enhancement corresponding to BPH.
PI-RADS v2 Assessment: Transition Zone (TZ)
| T2W | DWI | PI-RADS |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | |
| 2 | 2 | |
| 3 | ≤4 5 |
3 4 |
| 4 | 4 | |
| 5 | 5 |
The transition zone surrounds the prostatic urethra and enlarges in aging men as a result of benign prostatic hyperplasia. For the transition zone the T2w imaging is the primary determining sequence (dominant sequence) to assign the PI-RADS assessment category.
In the transitional zone an equivocal lesion (PI-RADS category 3) is assigned to PI-RADS category 4 if the DWI corresponds with category 5 (markedly intense greater than 1.5cm). The lesion remains assigned to PI-RADS category 3 if the DWI corresponds to DWI category 4 (markedly intense but less than 1.5cm) or a lower category.
PI-RADS v2 Assessment of DWI
| Score | Peripheral Zone (PZ) or Transition Zone (TZ) |
|---|---|
| 1 | No abnormality (i.e., normal) on ADC and high b-value DWI |
| 2 | Indistinct hypointense on ADC |
| 3 | Focal mildly/moderatly hypointense on ADC and isointense/mildly hyperintense on high b-value DWI |
| 4 | Focal markedly hypointense on ADC and markedly hyperintense on high b-value DWI; <1.5cm in greatest dimenson |
| 5 | Same as 4 but ≥1.5cm in greatest dimension or definite extraprostatic extension/invasive behavior |
PI-RADS v2 Assessment of T2W-TZ
| Score | Transition Zone (TZ) |
|---|---|
| 1 | Homogeneous intermediate signal intensity (normal) |
| 2 | Circumscribed hypointense or heterogeneous encapsulated nodule(s) (BPH) |
| 3 | Heterogeneous signal intensity with obscured margins; includes others that doe not qualify as 2, 4, or 5 |
| 4 | Lenticular or non-circumscribed, homogeneous, moderately hypointense, and <1.5cm in greatest dimension |
| 5 | Same as 4 but ≥1.5cm in greatest dimension or definite extraprostatic extension/invasive behavior |
- Weinreb JC, Barentsz JO, Choyke PL, et al. PI-RADS Prostate Imaging – Reporting and Data System: 2015, Version 2. European Urology 2016; 69:16-40